* How to select the pore size of the insert membrane product with chamber?
First, you need to determine whether the application you are carrying out requires cells to pass through the pores in the chamber membrane. In generally, the co-culture experiments, CACO-2 Transport experiments and the construction of cell polarization models do not require the cell to penetrate the membrane, and most of them choose products with small pore sizes such as 0.4um or 1.0um. However, in cell migration and invasion assay, cells need to pass through the membrane of the upper chamber and reach the dorsal side of the membrane (in a few cases, they will fall into the lower chamber, such as the migration/invasion assay of suspension cells). Therefore, larger pore size is required (for example, products with 8um pore size are often selected in the migration and invasion assay of tumor cells).
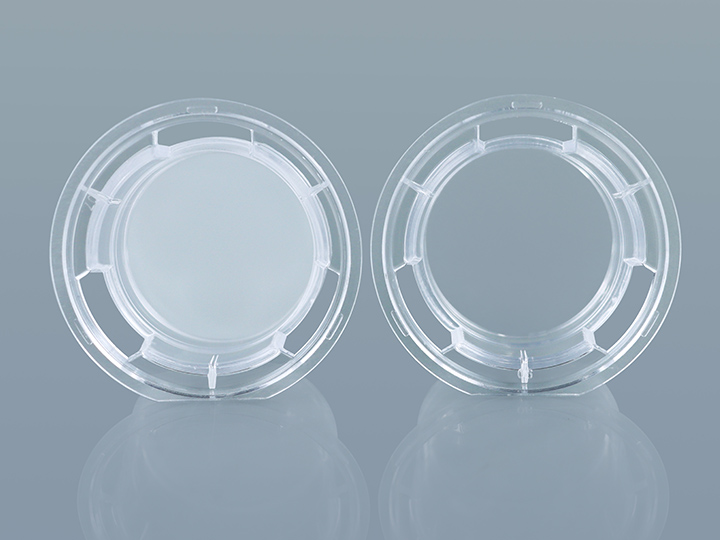
* How to select the material of the chamber membrane?
There are two kinds of membrane materials, polycarbonate (PC) and polyesteror polyethyleneterephthalate (PET), for Jet Biofil chamber products.
PC and PET membrane materials are widely used. The main difference between them is in light permeability, that is, PC membrane is translucent, which is not convenient to observe the morphology of upper chamber cells in the process of culture; PET membrane is transparent, which is convenient to observe the state of cells under phase contrast microscope.
In addition, at the pore size of 0.4um, the pore density (number of pores per unit area) of PC membrane and PET membrane is different, and PC membrane provides higher membrane pore density. You can choose according to the requirements of the experiment (whether you need to observe the cell state and whether you need a membrane with higher pore density).
* If the membrane material of the chamber is different from that of the cell culture dish/bottle, will there be any difference in the cell adhesion?
Although the material of the uncoated chamber membrane (PC or PET) is different from that of the ordinary plastic cell culture dishes/bottles (Polystyrene, PS), both sides of the membrane are subject to tissue culture treated (TC Treated), which is the same as the surface treatment of PS supplies for cell culture. Therefore, under normal circumstances, the cell adhesion in the chamber should be similar to that in the culture dish/bottle. In general culture, cells that need to be coated with the matrix proteins to auxiliary adhesion still need to be coated on the chamber. The coating method is similar to the common culture surface, and the amount of coating liquid required can be converted by the surface area of chamber membrane
* Can the products with the chamber be reused after sterilization?
Products with the chamber are single-use supplies and cannot be reused. The materials of the well plate and membrane of the chamber cannot withstand high-pressure steam sterilization, and it cannot be confirmed whether the reused chamber is thoroughly cleaned, so the experimental effect of reuse cannot be guaranteed.
* Does the chamber of insert membrane need to be matched with special receiving plate/lower chamber products?
It is suitable for ordinary cell culture perforated plates of corresponding specifications (such as TCP010006, TCP010012, TCP010024, etc.).
* Is it necessary to conduct “hydration” before cell inoculation?
Most applications do not require additional “hydration” operation. This operation is mainly used for the invasion chamber pre-coated with Matrigel, which needs to be balanced to room temperature before use, and added with a serum free medium pre-heated to 37℃, and hydrated in the incubator for two hours.
In a few cases, adding medium in the upper and lower chambers in advance and preincubating in the incubator for more than 1 hour can help cells adhere to the wall, but most cells can be directly inoculated.
* What is the liquid adding sequence of inoculated cells?
Generally, the preheated medium is first added to the pore (lower chamber) of perforated plate, and then the chamber is gently put into the pore. When placing, it is recommended to tilt the chamber slightly, with one side touching the liquid level first, so as to prevent bubbles from forming under the chamber placed vertically. After that, the uniformly mixed cell suspension can be added into the chamber.
* Since there are many pores on the chamber membrane, will the liquid be leaked to the lower chamber quickly when matrix protein is coated or some liquid is added to the upper chamber alone?
Generally not. The pore diameter on the membrane of the chamber is limited. Under the effect of surface tension, the coating liquid added to the upper chamber will not be leaked out quickly. If a large amount of liquid is found dripping in a short time, please check whether the membrane of the chamber is cracked or incomplete
* In co-culture experiment, how to arrange the position of cells inoculated in upper and lower chambers?
Because of the existence of pores on the chamber membrane, the culture medium of the upper and lower chambers can communicate with each other, and the cells inoculated in the upper and lower chambers interact with each other. The position arrangement of cells to be inoculated should take into account the convenience of collecting cells and conducting downstream detection, as well as the difference between the culture areas of the upper and lower chambers (the effective growth area of the upper chamber is smaller than that of the lower chamber, and accordingly, the number of cells to be inoculated may vary). You can refer to relevant literatures or conduct preliminary experiments to finally decide the experimental arrangement.
* Can the cells inoculated in the chamber be digested and collected?
Yes. You can use reagents (such as trypsin, etc.) that digest corresponding cells in ordinary culture vessels, and add the recommended volume of digestive fluids into both upper and lower chambers
*When the cells inoculated in the chamber are treated with drugs, does the drug only need to be added to the upper chamber?
Due to the existence of pores on the chamber membrane, we suggest that you add culture media containing the same concentration of drugs in both upper and lower chambers to ensure your drug treatment concentration.